 Let’s be honest. Reverse psychology marketing isn’t for everyone. Only those who are ready to challenge the status quo and think outside the box should even consider leveraging this approach.
Let’s be honest. Reverse psychology marketing isn’t for everyone. Only those who are ready to challenge the status quo and think outside the box should even consider leveraging this approach.
Still reading? Congratulations! You’ve just experienced a little reverse psychology in action and now know first-hand just how effective it can be. If you’re really ready for an advanced tactic like this and the results it can help you achieve, give me a few minutes and I’ll walk you through how to integrate reverse psychology into your own marketing strategy.
Understanding Reverse Psychology in Marketing
Reverse psychology in marketing is a strategy that involves encouraging consumers to do the opposite of what they are being told. It leverages the human tendency to assert independence and make decisions contrary to explicit instructions, especially when they feel their freedom of choice is being limited.
The Fundamentals of Reverse Psychology
Reverse psychology taps into psychological principles, such as reactance theory, which suggests that when people perceive their freedoms are being restricted, they are motivated to restore them. This can lead to a paradoxical outcome where telling someone not to do something makes them more likely to do it.
Reverse Psychology in Marketing
In the context of marketing, reverse psychology is used to create a sense of autonomy and empowerment in the consumer. Instead of using traditional persuasive techniques that overtly push a product or service, marketers might subtly suggest that the product might not be for everyone or that it is in limited supply, thereby triggering a desire in the consumer to prove their uniqueness or seize a scarce opportunity.
Reverse Psychology vs. Traditional Marketing Approaches
Traditional marketing typically involves direct promotion of the product’s benefits, features, and value propositions. It employs persuasive language and clear calls to action and often relies on creating a sense of need or urgency.
Contrarily, reverse psychology in marketing might involve statements like “This product isn’t for everyone” or “Only for those who truly appreciate quality,” which can prompt consumers to want to prove that they are the exception. It’s about creating intrigue and a sense of challenge, a core aspect of contrarian marketing approaches.
The Psychology Behind Customer Decisions
Customer decisions are influenced by a complex interplay of cognitive, emotional, and social factors. Here are some key psychological principles:
- Cognitive Biases: These are systematic patterns of deviation from norm or rationality in judgment. Common biases include:
- Anchoring: Relying heavily on the first piece of information encountered.
- Confirmation Bias: Favoring information that confirms existing beliefs.
- Scarcity Effect: Perceiving scarce items as more valuable.
- Decision Fatigue: As people make more decisions, their ability to make subsequent decisions deteriorates. This is why simplifying choices can lead to better customer experiences.
- Social Proof: People tend to follow the actions of others. Reviews, testimonials, and user-generated content can significantly influence decisions.
How Emotions Influence Purchasing Behavior
Emotions play a critical role in purchasing decisions, often more than rational analysis. Let’s take a quick look at some ways emotions influence behavior, a key aspect of advertising psychology.
- Positive Emotions: Happiness, excitement, and a sense of belonging can drive purchases. Marketing that evokes these emotions can create a strong connection with the brand. Coca-Cola, for instance, leverages this approach almost exclusively.
- Negative Emotions: Fear, guilt, and urgency can also be powerful motivators. For instance, security companies often use fear-based marketing, highlighting risks to promote their solutions.
- Emotional Triggers: Specific triggers like nostalgia, empathy, or humor can be used to create memorable marketing campaigns. For instance, John Lewis’s Christmas adverts in the UK often use emotional storytelling to create a strong bond with viewers.
Leveraging Low-Volume Pullbacks in Marketing Strategies
Low-volume pullbacks involve creating an artificial sense of scarcity or exclusivity to drive demand. Let’s explore how to leverage this strategy effectively.
- Scarcity Principle: Highlighting limited availability can increase the perceived value of a product. For example, limited edition products or “only a few items left” messages can prompt quicker purchasing decisions.
- Exclusivity: Making a product or service seem exclusive can enhance its appeal. Club memberships, early access for subscribers, or invite-only events, for instance, create a sense of exclusivity that can drive interest and demand.
- Timed Offers: Time-limited deals can create urgency. For example, flash sales and countdown timers on websites encourage customers to act quickly.
- Personalization: Tailoring scarcity messages to individual customers based on their behavior and preferences can make them more effective. For instance, personalized emails that highlight a limited stock of items the customer has previously shown interest in.
Combining These Strategies
To maximize effectiveness, these principles should be combined strategically.
- Emotionally Charged Scarcity: Use emotionally compelling narratives to frame scarcity. For instance, a charity campaign might highlight the urgency and emotional impact of donations.
- Social Proof with Scarcity: Show how others are acting on the limited-time offer, reinforcing the social proof while emphasizing scarcity.
- Personalized Emotional Appeals: Use data-driven insights to create personalized messages that resonate emotionally while highlighting exclusivity or limited availability.
The Role of Social Media in Reverse Psychology Marketing
Social media marketing platforms are ideal for reverse psychology marketing due to their interactive nature and wide reach. Here’s how social media facilitates this approach.
- Viral Potential: Contrarian content can quickly go viral, reaching a large audience as people share, comment on, and engage with unexpected or provocative messages.
- Direct Interaction: Social media allows for real-time interaction with customers, making it easier to gauge responses and adjust strategies accordingly.
- Targeted Advertising: Platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and X (formerly known as Twitter) provide sophisticated targeting tools, enabling marketers to deliver reverse psychology messages to specific demographics and psychographics.
Engaging Audiences with Contrarian Content
Contrarian content is designed to challenge norms and expectations, making it highly engaging. You can leverage this approach in a variety of ways.
- Challenging Assumptions: Create posts that challenge common beliefs or assumptions about your product or industry. For example, a B2B service brand might post, “Our approach isn’t for everyone. Only those ready to grow should try it,” encouraging people to prove they are among the dedicated.
- Humor and Irony: Use humor and irony to make the contrarian message more palatable and shareable. For instance, Wendy’s X account often uses humor and sarcasm, playfully roasting customers and competitors, garnering a massive following and high engagement rates.
- Exclusivity and Scarcity: Highlight the exclusivity or limited availability of a product or service. For example, “Only 50 spots left in our elite coaching program. If you have to ask if you qualify, you probably don’t.”
- User-Generated Content: Encourage followers to share their stories or experiences that align with the contrarian message. For instance, a brand might run a campaign asking users to share times when they went against the norm and succeeded, using a unique hashtag to track submissions.
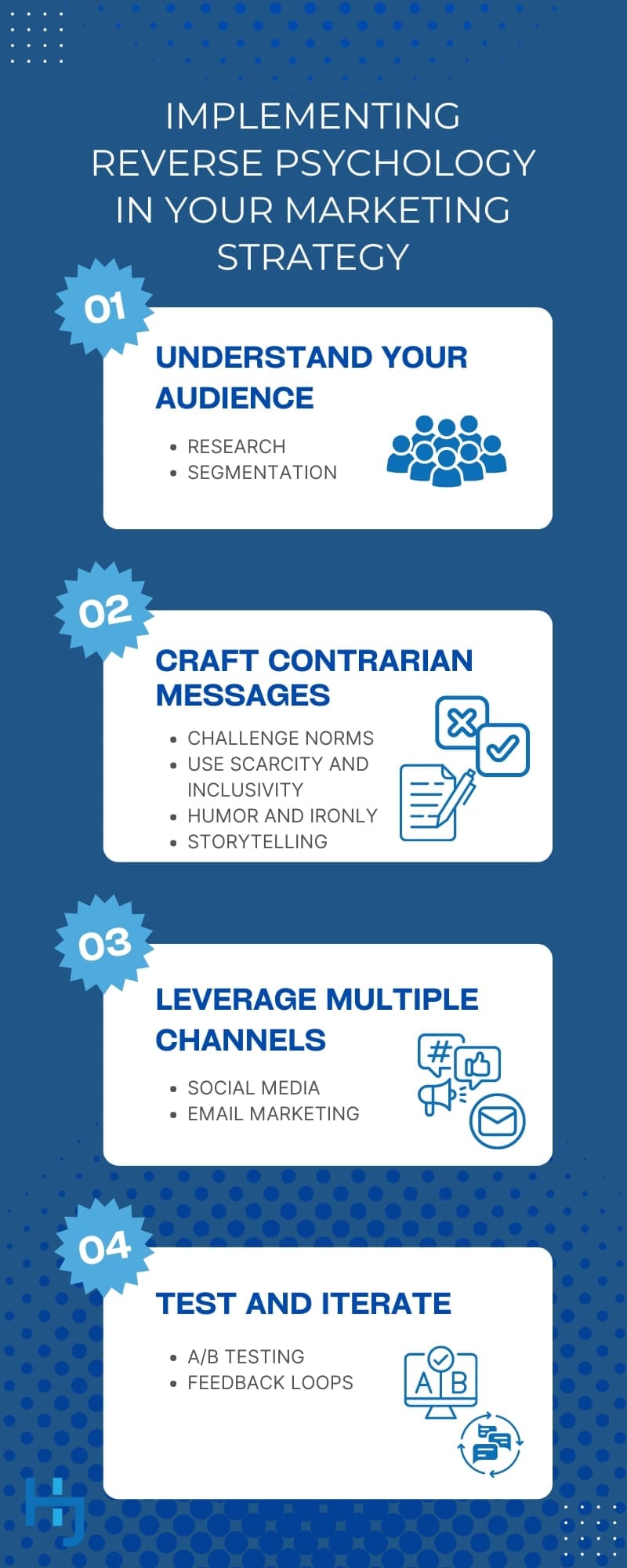
Implementing Reverse Psychology in Your Marketing Strategy
Reverse psychology in marketing involves using strategies that subtly prompt customers to act contrary to what they are explicitly told. This can create a sense of empowerment and intrigue, encouraging engagement and purchases.
Steps to Integrate Reverse Psychology Approaches
Now that we’ve covered the background, let’s explore the steps involved in integrating reverse psychology into your marketing.
1. Understand Your Audience
- Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand your audience’s preferences, behaviors, and pain points.
- Segmentation: Segment your audience to tailor messages that will resonate with different groups.
2. Craft Contrarian Messages
- Challenge Norms: Develop messages that challenge common beliefs or behaviors. For example, “Our product might not be for everyone” can intrigue potential customers.
- Use Scarcity and Exclusivity: Highlight limited availability or exclusive access to create urgency and desire.
- Humor and Irony: Use humor and irony to make contrarian messages more engaging. This approach can make your content more shareable.
- Storytelling: Use compelling narratives that incorporate reverse psychology elements, such as highlighting the benefits of not following the crowd.
3. Leverage Multiple Channels
- Social Media: Use platforms like Facebook, X, and Instagram to share your contrarian content. Engage with followers to build a community around your brand.
- Email Marketing: Craft email campaigns that use reverse psychology techniques, such as suggesting that the offer might not be for everyone.
4. Test and Iterate
- A/B Testing: Test different versions of your messages to see which resonates best with your audience.
- Feedback Loops: Collect and analyze feedback to continuously refine your approach.
Challenges and Considerations
To avoid potential missteps in your marketing strategy, keep the following considerations in mind while you plan and deploy initiatives.
Understanding Nuances
- Subtlety: Ensure your messages are subtle enough not to appear manipulative or disingenuous. Overly aggressive reverse psychology can backfire.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be mindful of cultural differences that might affect how your messages are received.
- Diverse Reactions: Recognize that not all customers will respond positively to reverse psychology. Tailor your approach based on audience segments.
Maintaining Brand Integrity
- Consistency: Ensure that your reverse psychology messages align with your overall brand voice and values.
- Transparency: Avoid misleading or deceptive tactics that could harm your brand’s reputation.
Tools and Metrics for Tracking Success
Tracking your results allows you to duplicate successes and eliminate strategies that aren’t effective for your brand. Below, we’ll explore some metrics and tools that can help.
![]()
Engagement Metrics
- Social Media Analytics: Use tools like Facebook Insights, X Analytics, and Instagram Insights to track likes, shares, comments, and overall engagement.
- Content Performance: Monitor how your contrarian posts perform compared to regular posts in terms of reach and engagement.
Conversion Metrics
- Google Analytics: Track website traffic, conversion rates, and user behavior to see if your reverse psychology tactics are driving desired actions.
- Conversion Tracking: Use platform-specific tools like Meta Pixel to measure the impact of your campaigns.
Sentiment Analysis
- Brand Monitoring Tools: Tools like Brandwatch, Hootsuite Insights, and Social Mention can help analyze the sentiment of your audience towards your reverse psychology content.
- Customer Feedback: Directly gather feedback through surveys and polls to understand customer perceptions.
A/B Testing
- Testing Platforms: Use platforms like Optimizely or VWO to conduct A/B tests on your website and marketing campaigns to determine which reverse psychology messages are most effective.
CRM and Email Analytics
- Email Platforms: Track open rates, click-through rates, and conversion rates using email marketing platforms like Mailchimp or HubSpot.
- Customer Relationship Management: Use customer relationship management (CRM) tools to track customer interactions and measure the long-term impact of your reverse psychology strategies.
Level Up Your Reverse Psychology Marketing Strategy
Implementing reverse psychology in your marketing strategy involves understanding your audience, crafting engaging and contrarian messages, leveraging multiple channels, and continuously testing and refining your approach. While there are challenges to consider, such as maintaining brand integrity and understanding audience nuances, the right strategies can help ensure your campaigns are successful. If you’d like help developing a comprehensive digital marketing strategy that includes tactics like reverse psychology, let’s talk. Contact me for a complimentary consultation.
Reverse Psychology Marketing FAQs
How does reverse psychology work in marketing?
Reverse psychology in marketing works by subtly prompting customers to take action contrary to explicit instructions, often by creating a sense of scarcity, exclusivity, or challenging common beliefs.
What are some examples of reverse psychology in marketing?
Examples include Apple's limited product releases, Volkswagen’s “Think Small” campaign, and humorous, contrarian social media posts by brands like Wendy’s.
Why is reverse psychology effective in marketing?
Reverse psychology in marketing taps into psychological principles such as reactance theory, making customers more likely to assert their freedom and make a purchase.
How can I implement reverse psychology in my marketing strategy?
Steps include understanding your audience, crafting contrarian messages, using scarcity and exclusivity, creating engaging content, and leveraging multiple channels.
What are the challenges of using reverse psychology in marketing?
Challenges include maintaining subtlety, cultural sensitivity, brand integrity, and ensuring the approach resonates positively with the target audience.
What metrics should I track to measure the success of reverse psychology marketing?
Metrics include engagement rates, conversion rates, sentiment analysis, and results from A/B testing and customer feedback.
Can reverse psychology backfire in marketing?
Yes, if the messages are too aggressive or perceived as manipulative, reverse psychology in marketing can harm the brand’s reputation and alienate customers.
What role does social media play in reverse psychology marketing?
Social media platforms are ideal for contrarian content due to their interactive nature, wide reach, and ability to engage directly with customers.
How can I use scarcity and exclusivity in reverse psychology marketing?
Highlighting limited availability, creating exclusive offers, and using time-limited deals can effectively create a sense of urgency and desire.




































































